intercept
监控和存根网络请求与响应。
提示:建议先阅读网络请求指南。
所有拦截器在每个测试前会自动清除。
语法
// 仅监控
cy.intercept(url)
cy.intercept(method, url)
cy.intercept(routeMatcher)
参数参见 url、 method 和 routeMatcher
// 监控并存根响应
cy.intercept(url, staticResponse)
cy.intercept(method, url, staticResponse)
cy.intercept(routeMatcher, staticResponse)
cy.intercept(url, routeMatcher, staticResponse)
参见 staticResponse 参数
// 监控、动态存根、请求修改等
cy.intercept(url, routeHandler)
cy.intercept(method, url, routeHandler)
cy.intercept(routeMatcher, routeHandler)
cy.intercept(url, routeMatcher, routeHandler)
参见 routeHandler 参数
// 指定请求和响应类型
type CustomRequest = {
kind: 'custom_request'
}
type CustomResponse = {
kind: 'custom_response'
}
cy.intercept<CustomRequest, CustomResponse>(url, (req) => {
req.body // 请求的.body将是CustomRequest类型
req.continue((res) => {
res.body // 响应的.body将是CustomResponse类型
})
})
用法
正确用法
// 监控
cy.intercept('/users/**')
cy.intercept('GET', '/users*')
cy.intercept({
method: 'GET',
url: '/users*',
hostname: 'localhost',
})
// 监控并存根响应
cy.intercept('POST', '/users*', {
statusCode: 201,
body: {
name: 'Peter Pan',
},
})
// 监控、动态存根、请求修改等
cy.intercept('/users*', { hostname: 'localhost' }, (req) => {
/* 对请求和/或响应进行操作 */
})
参数
method (String)
匹配特定的HTTP方法(GET、
POST、PUT等)。
如果未定义方法,Cypress默认会匹配所有请求。
url (String, Glob, RegExp)
指定要匹配的URL。示例参见匹配url。
或者,通过routeMatcher参数指定URL。
routeMatcher (RouteMatcher)
routeMatcher是一个对象,用于将传入的HTTP请求与拦截的路由匹配。
所有属性都是可选的,但设置的属性必须全部匹配才能拦截请求。如果向任何属性传递string,它将使用Cypress.minimatch和{ matchBase: true }选项进行全局匹配。
| 选项 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| auth | HTTP基本认证(包含username和password键的对象) |
| headers | HTTP请求头(对象) |
| hostname | HTTP请求主机名 |
| https | true:仅匹配安全(https://)请求,false:仅匹配非安全(http://)请求 |
| method | HTTP请求方法(默认匹配任何方法) |
| middleware | true:按定义顺序优先匹配路由,false:反向匹配路由(默认) |
| path | HTTP请求路径(主机名后,包含查询参数) |
| pathname | 类似path,但不包含查询参数 |
| port | HTTP请求端口(数字或数组) |
| query | 解析后的查询字符串(对象) |
| resourceType 已弃用 | 请求的资源类型。resourceType可能值列表参见"请求对象属性"。 |
| times | 最大匹配次数(数字) |
| url | 完整�的HTTP请求URL |
示例参见下文使用RouteMatcher。
staticResponse (StaticResponse)
通过传递StaticResponse作为最后一个参数,可以为匹配的请求静态定义(存根)响应。属性列表参见StaticResponse对象。
此外,可以在StaticResponse中传递{ log: false }来禁用此拦截的命令日志。参见禁用请求日志。
routeHandler (Function)
每当请求匹配时,会调用routeHandler函数,第一个参数是请求对象。在回调中,可以访问整个请求-响应周期,修改传出请求、发送响应、访问真实响应等。
参见"拦截的请求"和使用routeHandler修改请求/响应。
生成结果
示例
匹配url
可以提供精确的URL进行匹配,或使用模式匹配一次匹配多个URL,可以是glob或正则表达式。参见URL的Glob模式匹配。
// 匹配完全符合URL的任何请求
cy.intercept('https://prod.cypress.io/users')
// 匹配满足glob模式的任何请求
cy.intercept('/users?_limit=*')
// 匹配满足正则模式的任何请求
cy.intercept(/\/users\?_limit=(3|5)$/)
匹配method
如果不传递method参数,则会匹配所有HTTP方法(GET、POST、PUT、PATCH、DELETE等)。
cy.intercept('/users')
// 匹配: GET http://localhost/users
// 也匹配: POST http://localhost/users
cy.intercept('GET', '/users')
// 匹配: GET http://localhost/users
// 但不匹配: POST http://localhost/users
使用RouteMatcher匹配
通过向cy.intercept传递routeMatcher对象,也可以实现指定method和url进行匹配:
// 两者结果相同:
cy.intercept({ method: 'GET', url: '**/users' })
cy.intercept('GET', '**/users')
// 匹配路径名为`/search`且查询参数为'q=some+terms'的任何类型请求
cy.intercept({
pathname: '/search',
query: {
q: 'some terms',
},
}).as('searchForTerms')
cy.intercept(
{
// 此正则匹配任何以'http://api.example.com/'开头并以'/edit'或'/save'结尾的URL
url: /^http:\/\/api\.example\.com\/.*\/(edit|save)/,
// 匹配的请求还必须包含此请求头
headers: {
'x-requested-with': 'exampleClient',
},
}
)
// 此示例将使1次对`/temporary-error`的请求收到网络错误,后续请求将不匹配此`RouteMatcher`
cy.intercept({ url: '/temporary-error', times: 1 }, { forceNetworkError: true })
模式匹配
// 使用glob匹配更新`/users`端点
cy.intercept({
method: '+(PUT|PATCH)',
url: '**/users/*',
})
// 匹配:
// PUT /users/1
// PATCH /users/1
//
// 不匹配:
// GET /users
// GET /users/1
// 同上,但使用正则
cy.intercept({
method: '/PUT|PATCH/',
url: '**/users/*',
})
为拦截的路由设置别名
虽然cy.intercept不返回任何内容,但可以链式调用.as创建别名,用于等待请求。
cy.intercept('GET', '/users').as('getAllUsers')
cy.intercept('POST', '/users').as('createUser')
为单个请求设置别名
可以通过设置拦截请求的alias属性为每个请求设置别名。这在拦截GraphQL请求时特别有用:
cy.intercept('POST', '/graphql', (req) => {
if (req.body.hasOwnProperty('query') && req.body.query.includes('mutation')) {
req.alias = 'gqlMutation'
}
})
// 断言已发出匹配的请求
cy.wait('@gqlMutation')
有关GraphQL请求别名的更多指导,参见使用GraphQL。
等待请求
使用cy.wait()和为拦截的路由设置别名等待请求/响应周期完成。
使用URL
cy.intercept('http://example.com/settings').as('getSettings')
// 一旦对获取设置的请求响应,'cy.wait'将解析
cy.wait('@getSettings')
使用RouteMatcher
cy.intercept({
url: 'http://example.com/search*',
query: { q: 'expected terms' },
}).as('search')
// 一�旦任何类型的搜索请求(查询字符串包含'q=expected+terms')响应,'cy.wait'将解析
cy.wait('@search')
使用返回的对象
在cy.intercept()路由别名上使用cy.wait()会返回一个表示请求/响应周期的拦截对象:
cy.wait('@someRoute').then((interception) => {
// 'interception'是一个包含'id'、'request'和'response'属性的对象
})
可以链式调用.its()和.should()对请求/响应周期进行断言:
// 断言对此路由的请求体包含'user'
cy.wait('@someRoute').its('request.body').should('include', 'user')
// 断言对此路由的请求收到HTTP状态码500的响应
cy.wait('@someRoute').its('response.statusCode').should('eq', 500)
// 断言对此路由的请求收到包含'id'的响应体
cy.wait('@someRoute').its('response.body').should('include', 'id')
等待错误
可以使用cy.wait()等待以网络错误结束的请求:
cy.intercept('GET', '/should-err', { forceNetworkError: true }).as('err')
// 断言此请求发生并以错误结束
cy.wait('@err').should('have.property', 'error')
存根响应
使用字符串
// 对'/update'的请求将以"success"作为响应体完成
cy.intercept('/update', 'success')
使用fixture
// 对'/users.json'的请求将以"users.json" fixture的内容完成
cy.intercept('/users.json', { fixture: 'users.json' })
使用StaticResponse对象
StaticResponse对象表示对HTTP请求的响应,可用于存根路由:
const staticResponse = {
/* 此处为一些StaticResponse属性... */
}
cy.intercept('/projects', staticResponse)
使用JSON体存根响应:
cy.intercept('/projects', {
body: [{ projectId: '1' }, { projectId: '2' }],
})
同时存根头、状态码和体:
cy.intercept('/not-found', {
statusCode: 404,
body: '404 Not Found!',
headers: {
'x-not-found': 'true',
},
})
使用读取为Buffer的fixture存根响应:
cy.intercept('/not-found', {
fixture: 'media/gif.mp4,null',
})
使用**routeHandler**函数
通过向cy.intercept的最后一个参数指定routeHandler函数,可以访问整个请求-响应会话,从而能够修改传出请求、操作真实响应、进行断言等。
routeHandler将传入的HTTP请求(IncomingHTTPRequest)作为第一个参数。
cy.intercept('/users*', (req) => {
/* 对请求和/或响应进行操作 */
})
在这些示例中,我们将传入的HTTP请求称为req。熟悉Express.js中间件语法的用户应该对此语法感到熟悉。
对请求进行断言
cy.intercept('POST', '/organization', (req) => {
expect(req.body).to.include('Acme Company')
})
修改传出请求
可以使用请求处理程序回调在发送之前修改拦截的请求对象。
// 在发送到目标之前将请求体设置为不同的内容
cy.intercept('POST', '/login', (req) => {
req.body = 'username=janelane&password=secret123'
})
// 动态设置别名
cy.intercept('POST', '/login', (req) => {
req.alias = 'login'
})
向传出请求添加头
可以向传出请求添加头,或修改现有头
cy.intercept('/req-headers', (req) => {
req.headers['x-custom-headers'] = 'added by cy.intercept'
})
注意:新头不会显示在浏览器的网络标签中,因为请求已经离开浏览器。仍然可以通过如下等待拦截来确认头已添加:
等待拦截
cy.intercept('/req-headers', (req) => {
req.headers['x-custom-headers'] = 'added by cy.intercept'
}).as('headers')
// 应用程序发出调用...
// 确认自定义头已添加
cy.wait('@headers')
.its('request.headers')
.should('have.property', 'x-custom-headers', 'added by cy.intercept')
向所有传出请求添加、修改或删除头
可以使用supportFile中的beforeEach()向所有传出请求添加、修改或删除头。
beforeEach(() => {
cy.intercept(
{ url: 'http://localhost:3001/**', middleware: true },
// 从所有传出请求中删除'if-none-match'头
(req) => delete req.headers['if-none-match']
)
})
动态存根响应
可以使用req.reply()函数动态控制对请求的响应。
cy.intercept('/billing', (req) => {
// 'req'上的函数可用于在此动态响应请求
// 将请求发送到目标服务器
req.reply()
// 用JSON对象响应请求
req.reply({ plan: 'starter' })
// 将请求发送到目标服务器并拦截响应
req.continue((res) => {
// 'res'表示真实目标的响应
// 更多详情和示例参见"拦截响应"
})
})
更多关于req对象及其属性和方法的信息,参见"拦截的请求"。
返回Promise
如果从路由回调返回Promise,它将在继续请求之前被等待。
cy.intercept('POST', '/login', (req) => {
// 可以异步获取测试数据...
return getLoginCredentials().then((credentials) => {
// ...然后使用它补充传出请求
req.headers['authorization'] = credentials
})
})
将请求传递给下一个请求处理程序
如果在请求处理程序中没有显式调用req.reply()或req.continue(),请求将传递给下一个请求处理程序,直到没有剩余。
// 可以有一个顶层的中间件处理程序,在所有请求上设置认证令牌
// 但记住设置`middleware: true`会导致它总是首先被调用
cy.intercept('http://api.company.com/', { middleware: true }, (req) => {
req.headers['authorization'] = `token ${token}`
})
// 然后有另一个更窄地断言某些请求的处理程序
cy.intercept('POST', 'http://api.company.com/widgets', (req) => {
expect(req.body).to.include('analytics')
})
// 对http://api.company.com/widgets的POST请求会触发这两个回调,中间件优先,然后请求会带着修改后的请求头发送到真实目标
禁用请求的日志
默认情况下,Cypress会记录匹配任何cy.intercept()的所有请求,以及所有XMLHttpRequest和fetch请求。可以通过在第二个参数中传递{ log: false }来使用cy.intercept()禁用这些日志:
// 禁用Cypress默认记录所有XMLHttpRequest和fetch的行为
cy.intercept({ resourceType: /xhr|fetch/ }, { log: false })
注意:目前只能在定义cy.intercept()时启用/禁用请求的日志,不能在intercept回调中。参见#26069。
拦截响应
在传递给req.continue()的回调中,可以访问目标服务器的真实响应。
cy.intercept('/integrations', (req) => {
// 带回调的req.continue()会将请求发送到目标服务器
req.continue((res) => {
// 'res'表示真实目标的响应
// 可以在发送到浏览器之前操作'res'
})
})
更多关于res对象的信息,参见"拦截的响应"。更多关于req.continue()的信息,参见"使用req.continue()控制传出请求"�。
对响应进行断言
cy.intercept('/projects/2', (req) => {
req.continue((res) => {
expect(res.body).to.include('My Project')
})
})
返回Promise
如果从路由回调返回Promise,它将在将响应发送到浏览器之前被等待。
cy.intercept('/users', (req) => {
req.continue((res) => {
// 在'waitForSomething()'解析之前,响应不会发送到浏览器
return waitForSomething()
})
})
限制或延迟所有传入响应
可以使用supportFile中的beforeEach()限制或延迟所有传入响应。
// 限制API响应以模拟真实条件
beforeEach(() => {
cy.intercept(
{
url: 'http://localhost:3001/**',
middleware: true,
},
(req) => {
req.on('response', (res) => {
// 将响应限制为1 Mbps以模拟移动3G连接
res.setThrottle(1000)
})
}
)
})
使用routeHandler修改请求/响应
将routeHandler作为最后一个参数指定,以修改传出请求、存根响应、进行断言等。
如果向routeHandler传递函数,它将使用拦截的HTTP请求req作为第一个参数调用:
cy.intercept('/api', (req) => {
// 对拦截的请求进行操作
})
从这里,可以对拦截的请求进行以下操作:
对请求进行断言
可以使用请求处理程序回调在发送之前对拦截的请求对象进行断言。
// 匹配创建用户的请求
cy.intercept('POST', '/users', (req) => {
// 对负载��内容进行断言
expect(req.body).to.include('Peter Pan')
})
控制传出请求
可以在发送之前修改传出请求的体、头等。
// 在发送到目标之前修改请求体
cy.intercept('POST', '/users', (req) => {
req.body = {
name: 'Peter Pan',
}
})
// 向传出请求添加头
cy.intercept('POST', '/users', (req) => {
req.headers['x-custom-header'] = 'added by cy.intercept'
})
// 修改现有头
cy.intercept('POST', '/users', (req) => {
req.headers['authorization'] = 'Basic YWxhZGRpbjpvcGVuc2VzYW1l'
})
验证请求修改
cy.intercept('POST', '/users', (req) => {
req.headers['x-custom-header'] = 'added by cy.intercept'
}).as('createUser')
cy.get('button.save').click()
// 可以通过在命令日志中选择此行在控制台输出中查看头:
cy.wait('@createUser')
// ...或进行断言:
.its('request.headers')
.should('have.property', 'x-custom-header', 'added by cy.intercept')
无法通过检查浏览器的网络流量(例如在Chrome开发者工具中)验证请求修改,因为浏览器在Cypress可以拦截之前记录网络流量。
无法使用cy.request()调试cy.intercept()!Cypress仅拦截由前端应用程序发出的请求。
控制响应
传递给路由处理程序的拦截请求(以下称为req,尽管可以使用任何名称��)包含动态控制请求响应的方法:
req.reply()- 存根响应,无需依赖真实后端req.continue()- 修改或对真实响应进行断言req.destroy()- 销毁请求并以网络错误响应req.redirect()- 以重定向到指定位置响应请求req.on()- 通过附加事件修改响应
存根响应(req.reply()):
req.reply()的第一个参数是StaticResponse对象:
// 不依赖真实后端存根响应
cy.intercept('POST', '/users', (req) => {
req.reply({
headers: {
Set-Cookie: 'newUserName=Peter Pan;'
},
statusCode: 201,
body: {
name: 'Peter Pan'
},
delay: 10, // 毫秒
throttleKbps: 1000, // 模拟3G连接
forceNetworkError: false // 默认
})
})
// 使用fixture存根响应体
cy.intercept('GET', '/users', (req) => {
req.reply({
statusCode: 200, // 默认
fixture: 'users.json'
})
})
更多信息参见StaticResponse对象。
reply方法也支持简写,避免必须指定StaticResponse对象:
// 等同于`req.reply({ body })`
req.reply(body)
// 等同于`req.reply({ body, headers })`
req.reply(body, headers)
// 等同于`req.reply({ statusCode, body, headers})`
req.reply(statusCode, body, headers)
注意:调用reply()将结束请求阶段并阻止请求传播到下一个匹配的请求处理程序。参见拦截生命周期。
修改真实响应(continue):
continue方法接受一个函数,该函数传递一个表示在返回客户端(前端应用程序)时被拦截的真实响应的对象。
// 传递请求并对真实响应进行断言
cy.intercept('POST', '/users', (req) => {
req.continue((res) => {
expect(res.body).to.include('Peter Pan')
})
})
以网络错误响应(destroy):
// 动态销毁请求并以网络错误响应
cy.intercept('POST', '/users', (req) => {
if (mustDestroy(req)) {
req.destroy()
}
function mustDestroy(req) {
// 基于`req`内容决定是否强制网络错误的代码
}
})
以新位置响应(redirect):
// 以重定向到新'location'响应此请求
cy.intercept('GET', '/users', (req) => {
// statusCode默认为`302`
req.redirect('/customers', 301)
})
通过监听事件响应(on):
cy.intercept('GET', '/users', (req) => {
req.on('before:response', (res) => {
// 当触发`before:response`事件时执行操作
})
})
cy.intercept('POST', '/users', (req) => {
req.on('response', (res) => {
// 当触发`response`事件时执行操作
})
})
返回Promise
如果从路由回调返回Promise,它将在继续请求之前被等待。
cy.intercept('POST', '/users', (req) => {
// 异步获取测试数据
return getAuthToken().then((token) => {
// ...并将其应用于传出请求
req.headers['Authorization'] = `Basic ${token}`
})
})
cy.intercept('POST', '/users', (req) => {
req.continue((res) => {
// 在`waitForSomething()`解析之前,响应不会发送到浏览器:
return waitForSomething()
})
})
使用字符串存根响应
// 创建用户的请求将以'success'作为响应体完成
cy.intercept('POST', '/users', 'success')
// { body: 'success' }
拦截的请求
如果向cy.intercept()的处理程序传递函数,第一个参数将是表示拦截的HTTP请求的对象:
cy.intercept('/api', (req) => {
// `req`表示拦截的HTTP请求
})
从这里,可以对拦截的请求进行以下操作:
- 可以修改并对请求的属性(体、头、URL、方法...)进行断言
- 请求可以发送到真实的上游服务器
- 可选地,可以拦截此响应
- 可以提供响应以存根请求
- 可以为请求的各种事件附加监听器
请求对象属性
请求对象(req)具有HTTP请求本身的几个属性:
{
/**
* 请求的体。
* 如果使用JSON Content-Type且体是有效的JSON,
* 这将是一个对象。
* 如果体是二进制内容,这将是一个buffer。
*/
body: string | object | any
/**
* 请求的头。
*/
headers: { [key: string]: string }
/**
* 请求的HTTP方法(GET、POST等)。
*/
method: string
/**
* 请求的URL。
*/
url: string
/**
* URL查询字符串作为对象。
*/
query: Record<string, string|number>
/**
* 请求中使用的HTTP版本。只读。
*/
httpVersion: string
/**
* 请求的资源类型。只读。
*/
resourceType: 'document' | 'fetch' | 'xhr' | 'websocket' | 'stylesheet'
| 'script' | 'image' | 'font' | 'cspviolationreport' | 'ping'
| 'manifest' | 'other'
}
req还有一些可选属性,可以设置以控制Cypress特定的行为:
{
/**
* 如果提供,上游响应此请求的超时毫秒数。
* 默认使用配置中的`responseTimeout`。
*/
responseTimeout?: number
/**
* 设置此请求发出时是否应遵循重定向。
* 默认情况下,请求在产生响应之前不会遵循重定向(产生3xx重定向)。
*/
followRedirect?: boolean
/**
* 如果设置,可以使用`cy.wait`通过`cy.wait('@alias')`等待此请求/响应周期完成。
*/
alias?: string
}
对req属性的任何修改将持久化到其他请求处理程序,并最终合并到实际的传出HTTP请求中。
使用req.continue()控制传出请求
不带任何参数调用req.continue()将导致请求被发出,响应将在任何其他监听器被调用后返回到浏览器。例如,以下代码修改POST请求然后将其发送到上游服务器:
cy.intercept('POST', '/submitStory', (req) => {
req.body.storyName = 'some name'
// 发送修改后的请求并跳过任何其他匹配的请求处理程序
req.continue()
})
如果向req.continue()传递函数,请求将被发送到真实的上游服务器,回调将在从服务器完全接收到响应时调用。参见"拦截的响应"
注意:调用req.continue()将阻止请求传播到下一个匹配的请求处理程序。更多信息参见"拦截生命周期"。
使用req.reply()提供存根响应
req.reply()函数可用于为拦截的请求发送存根响应。通过向req.reply()传递字符串、对象或StaticResponse,可以阻止请求到达目标服务器。
例如,以下代码从请求拦截器存根JSON响应:
cy.intercept('/billing', (req) => {
// 在请求时动态获取账单计划名称
const planName = getPlanName()
// 此对象将自动被JSON.stringify并作为响应发送
req.reply({ plan: planName })
})
除了向req.reply()传递普通对象或字符串,还可以传递StaticResponse对象。使用StaticResponse,可以强制网络错误、延迟/限制响应、发送fixture等。
例如,以下代码以500ms的延迟提供动态选择的fixture:
cy.intercept('/api/users/*', async (req) => {
// 在请求时异步获取fixture文件名
const fixtureFilename = await getFixtureFilenameForUrl(req.url)
req.reply({
fixture: fixtureFilename,
delay: 500,
})
})
更多关于以这种方式存根响应的信息,参见StaticResponse文档。
req.reply()简写
req.reply()也支持简写,类似于res.send(),避免必须指定StaticResponse对象:
// 等同于`req.reply({ body })`
req.reply(body)
// 等同于`req.reply({ body, headers })`
req.reply(body, headers)
// 等同于`req.reply({ statusCode, body, headers})`
req.reply(statusCode, body, headers)
便利函数
req上还有两个便利函数:
{
/**
* 销毁请求并以网络错误响应。
*/
destroy(): void
/**
* 以重定向到新'location'响应此请求。
* @param statusCode 重定向的HTTP状态码。默认:302
*/
redirect(location: string, statusCode?: number): void
}
示例参见控制响应部分
注意:调用req.reply()将结束请求阶段并阻止请求传播到下一个匹配的请求处理程序。更多信息参见"拦截生命周期"。
请求事件
对于高级使用,req上有几个事件可用,代表拦截生命周期的不同阶段。
通过调用req.on,可以订阅不同的事件:
cy.intercept('/shop', (req) => {
req.on('before:response', (res) => {
/**
* 在`response`之前和任何`req.continue`处理程序之前触发。
* 对`res`的修改将应用于传入的响应。
* 如果返回Promise,它将在处理其他事件处理程序之前被等待。
*/
})
req.on('response', (res) => {
/**
* 在`before:response`之后和任何`req.continue`处理程序之后触发 - 在响应发送到浏览器之前。
* 对`res`的修改将应用于传入的响应。
* 如果返回Promise,它将在处理其他事件处理程序之前被等待。
*/
})
req.on('after:response', (res) => {
/**
* 一旦请求的响应完成发送到浏览器时触发。
* 对`res`的修改没有影响。
* 如果返回Promise,它将在处理其他事件处理程序之前被等待。
*/
})
})
更多关于res对象的信息,参见"拦截的响应"。更多关于请求排序的信息,参见"拦截生命周期"。
拦截的响应
可以通过两种方式拦截响应:
- 在请求处理程序内向
req.continue()传递回调 - 通过监听
before:response或response请求事件(参见"请求事件")
响应对象res将作为处理程序函数的第一个参数传递:
cy.intercept('/url', (req) => {
req.on('before:response', (res) => {
// 这将在任何`req.continue`或`response`处理程序之前调用
})
req.continue((res) => {
// 这将在所有`before:response`处理程序之后和任何`response`处理程序之前调用
// 通过调用`req.continue`,我们发出信号表示此请求处理程序将是最后一个,此时请求应被发出。
// 因此,每个请求只能有一个`req.continue`处理程序。
})
req.on('response', (res) => {
// 这将在所有`before:response`处理程序和`req.continue`处理程序之后调用
// 但在响应发送到浏览器之前
})
})
响应对象属性
传递给响应处理程序的响应对象(res)具有HTTP响应本身的几个属性。可以修改res上的所有以下属性:
| 属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| body | 响应体(object、string、ArrayBuffer) |
| headers | 响应头(object) |
| statusCode | 响应状态码(number) |
| statusMessage | 响应状态消息(string) |
关于body的注意:如果响应头包含Content-Type: application/json且体包含有效的JSON,这将是一个object。如果体包含二进制内容,这将是一个buffer。
res还有一些可选属性,可以设置以控制Cypress特定的行为:
| 属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| throttleKbps | 响应的最大数据传输速率(千比特/秒) |
| delay | 添加到响应时间的最小网络延迟或延迟(毫秒) |
对res属性的任何修改将持久化到其他响应处理程序,并最终合并到实际的传入HTTP响应中。
使用res.send()结束响应
要结束请求的响应阶段,调用res.send()。可选地,可以向res.send()传递StaticResponse,与实际响应合并。
当调用res.send()时,响应阶段将立即结束,当前请求的其他响应处理程序不会被调用。以下是res.send()的使用示例:
cy.intercept('/notification', (req) => {
req.continue((res) => {
if (res.body.status === 'failed') {
// 发送fixture体而不是现有的'res.body'
res.send({ fixture: 'success.json' })
}
})
})
更多关于格式的信息,参见StaticResponse文档。
res.send()简写
res.send()也支持简写,类似于req.reply(),避免必须指定StaticResponse对象:
// 等同于`res.send({ body })`
res.send(body)
// 等同于`res.send({ body, headers })`
res.send(body, headers)
// 等同于`res.send({ statusCode, body, headers})`
res.send(statusCode, body, headers)
便利函数
res上还有两个便利函数:
{
/**
* 在发送响应到客户端之前等待'delay'毫秒。
*/
setDelay: (delay: number) => IncomingHttpResponse
/**
* 以'throttleKbps'千比特/秒的速度提供响应。
*/
setThrottle: (throttleKbps: number) => IncomingHttpResponse
}
注意:调用res.send()将结束响应阶段并阻止响应传播到下一个匹配的响应处理程序。更多信息参见"拦截生命周期"。
StaticResponse对象
StaticResponse表示静态定义的响应(存根)。
StaticResponse上可用的属性如下。
| 选项 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| statusCode | HTTP响应状态码 |
| headers | HTTP响应头 |
| body | 提供静态响应体(object、string、ArrayBuffer)(当省略fixture时)。 |
| fixture | 提供fixture作为HTTP响应体(当省略body时允许)。以不同于文件类型默认值的编码读取内容时,传递fixture如path,encoding。 |
| forceNetworkError | 通过销毁浏览器连接强制错误 |
| delay | 添加到响应时间的最小网络延迟或延迟(毫秒) |
| throttleKbps | 响应的最大数据传输速率(千比特/秒) |
注意:所有属性都是可选的。
可以通过3种方式向Cypress提供StaticResponse:
- 作为
参数传递给cy.intercept(),存根路由的响应:cy.intercept('/url', staticResponse) - 传递给
req.reply(),从请求处理程序存根响应:req.reply(staticResponse) - 传递给
res.send(),从响应处理程序存根响应:res.send(staticResponse)
拦截生命周期
cy.intercept()拦截的生命周期始于从应用程序发送的HTTP请求匹配一个或多个注册的cy.intercept()路由。从那里,每个拦截有两个阶段:请求和响应。
cy.intercept()路由按定义的相反顺序匹配,除了定义为{ middleware: true }的路由,它们总是首先运行。这允许你通过定义重叠的cy.intercept()来覆盖现有的cy.intercept()声明:

请求阶段
以下步骤用于处理请求阶段。
- 根据上述算法(中间件优先�,然后是反向顺序的处理程序)从第一个匹配的路由开始。
- 是否向
cy.intercept()提供了处理程序(体、StaticResponse或函数)?如果没有,继续到步骤7。 - 如果处理程序是体或
StaticResponse,立即以该响应结束请求。 - 如果处理程序是函数,使用
req(传入的请求)作为第一个参数调用函数。更多关于req对象的信息,参见"拦截的请求"。- 如果调用
req.reply(),立即以提供的响应结束请求阶段。参见使用req.reply()提供存根响应。 - 如果调用
req.continue(),立即结束请求阶段,并将请求发送到目标服务器。如果向req.continue()提供了回调,它将在响应阶段被调用。
- 如果调用
- 如果处理程序返回Promise,等待Promise解析。
- 将对请求对象的任何修改与真实请求合并。
- 如果有另一个匹配的
cy.intercept(),返回到步骤2并继续执行该路由的步骤。 - 将请求发出到目标服务器并结束请求阶段。一旦收到响应,响应阶段将开始。
响应阶段
一旦从上游服务器收到HTTP响应,将应用以下步骤:
- 获取注册的
before:response事件监听器��列表。 - 对于每个
before:response监听器(如果有),使用res对象调用它。- 如果调用
res.send(),结束响应阶段并将任何传递的参数与响应合并。 - 如果返回Promise,等待它。将对响应属性的任何修改与真实响应合并。
- 如果调用
- 如果为此路由声明了带回调的
req.continue(),使用res对象调用回调。- 如果调用
res.send(),结束响应阶段并将任何传递的参数与响应合并。 - 如果返回Promise,等待它。将对响应属性的任何修改与真实响应合并。
- 如果调用
- 获取注册的
response事件监听器列表。 - 对于每个
response监听器(如果有),使用res对象调用它。- 如果调用
res.send(),结束响应阶段并将任何传递的参数与响应合并。 - 如果返回Promise,等待它。将对响应属性的任何修改与真实响应合并。
- 如果调用
- 将响应发送到浏览器。
- 一旦响应完成,获取注册的
after:response事件监听器列表。 - 对于每个
after:response监听器(如果有),使用res对象(减去res.send)调用它。- 如果返回Promise,等待它。
- 结束响应阶段。
URL的Glob模式匹配
当匹配URL时,提供精确的URL进行匹配可能限制性太强。例如,如果想在不同的主机上运行测试怎么办?
// 匹配完全符合URL的任何请求
cy.intercept('https://prod.cypress.io/users')
// 匹配: https://prod.cypress.io/users
// ...但不匹配: https://staging.cypress.io/users
// ...或: http://localhost/users
Glob模式匹配提供了必要的灵活性:
cy.intercept('/users')
// 匹配所有这些:
// https://prod.cypress.io/users
// https://staging.cypress.io/users
// http://localhost/users
cy.intercept('/users?_limit=+(3|5)')
// 匹配所有这些:
// https://prod.cypress.io/users?_limit=3
// http://localhost/users?_limit=5
Cypress.minimatch
在底层,cy.intercept使用minimatch库和{ matchBase: true }选项进行glob匹配,并通过Cypress全局提供访问。这使你可以在规范或Cypress浏览器控制台中测试模式。
可以仅用两个参数调用Cypress.minimatch - URL(string)和模式(string),如果返回true,则匹配!
expect(
Cypress.minimatch('http://localhost/users?_limit=3', '**/users?_limit=+(3|5)')
).to.be.true
expect(
Cypress.minimatch('http://localhost/users?_limit=5', '/users?_limit=+(3|5)', {
matchBase: true,
})
).to.be.true
expect(
Cypress.minimatch('http://localhost/users?_limit=7', '**/users?_limit=+(3|5)')
).to.be.false
minimatch选项
还可以传递选项(object)作为第三个参数,其中之一是debug,如果设置为true,将产生详细的输出,帮助你理解为什么模式不按预期工作:
Cypress.minimatch('http://localhost/users?_limit=3', '**/users?_limit=+(3|5)', {
debug: true,
})
// true (加上调试消息)
cy.intercept()和请求缓存
cy.intercept()在网络层拦截请求。当尝试拦截已被浏览器缓存的请求时,可能会导致混淆。如果请求从浏览器缓存提供,它将永远不会到达网络层,cy.intercept()也永远不会触发。
要查看是否影响你的应用程序,检查开发者工具。在以下示例中,所有红色圈出的请求已从缓存提供,不会发送HTTP请求。因此,它们不能被cy.intercept()拦截:
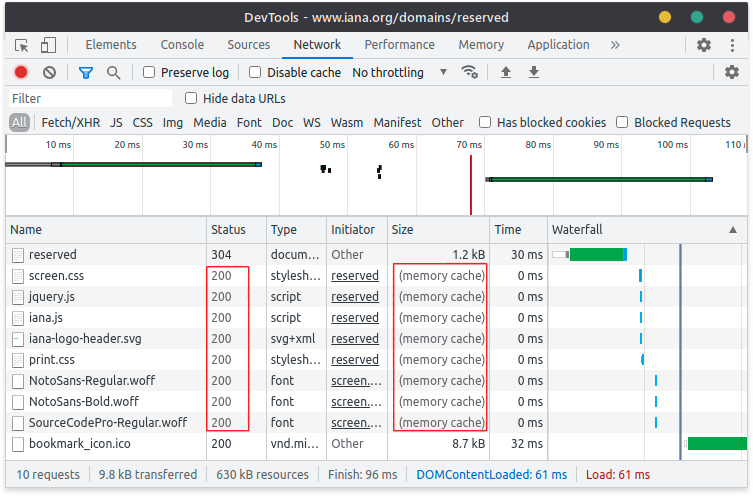
如果你想拦截通常发送缓存头的资源,以下是一些解决方法:
- 在测试模式下关闭开发服务器上的缓存头。
- 通过添加顶级
cy.intercept()从所需请求中删除缓存头来禁用响应缓存。例如:beforeEach(() => {
cy.intercept(
'https://api.example.com/**/*',
{ middleware: true },
(req) => {
req.on('before:response', (res) => {
// 强制所有API响应不被缓存
res.headers['cache-control'] = 'no-store'
})
}
)
}) - 仅限Chromium家族浏览器:使用
remote:debugger:protocol完全禁用缓存。更多信息,参见#14459问题上的此评论
命令日志
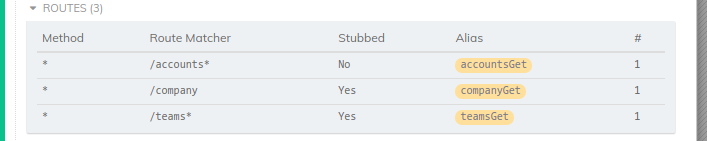
路由仪表板
当创建cy.intercept()规则时,Cypress将显示一个名为_Routes_的新仪表。
cy.intercept('/accounts*').as('accountsGet')
cy.intercept('/company', { companyId: 1 }).as('companyGet')
cy.intercept('/teams*', [{ teamId: 2 }]).as('teamsGet')
它将在仪表板中列出路由表,包括method、RouteMatcher、路由是否被存根、任何别名和匹配的请求数:
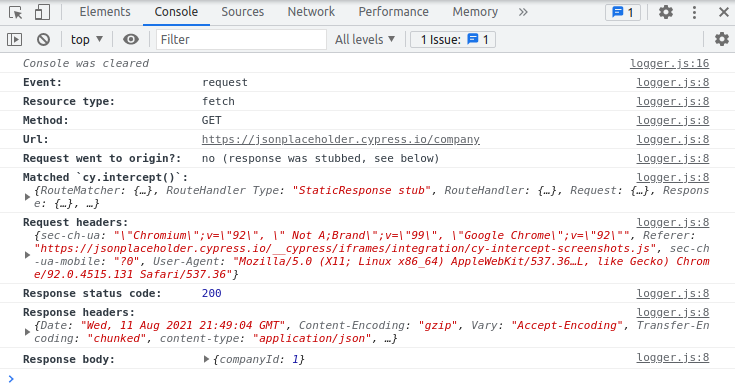
当发出HTTP请求时,Cypress会在命令日志中记录它们,并通过右侧黄色徽章的存在指示它们是否匹配cy.intercept():

圆形指示器填充表示请求到达了目标服务器,未填充表示请求被存根响应。
点击匹配cy.intercept()的请求将在控制台打印有关请求和响应的额外信息:
历史
| 版本 | 变更 |
|---|---|
| 14.0.0 | 弃用resourceType属性 |
| 12.2.0 | 向req和RouteMatcher添加resourceType属性。 |
| 7.6.0 | 向req(传递给请求处理程序函数的传入请求对象)添加query选项。 |
| 7.0.0 | 从RouteMatcher中移除matchUrlAgainstPath选项,反转处理程序顺序,添加请求事件,移除子字符串URL匹配,移除cy.route2别名,添加middleware RouteMatcher选项,重命名res.delay()为res.setDelay()和res.throttle()为res.setThrottle()。 |
| 6.4.0 | 将delayMs属性重命名为delay(向后兼容)。 |
| 6.2.0 | 向RouteMatcher添加matchUrlAgainstPath选项。 |
| 6.0.0 | 将cy.route2()重命名为cy.intercept()。 |
| 6.0.0 | 移除experimentalNetworkStubbing选项并使其成为默认行为。 |
| 5.1.0 | 在experimentalNetworkStubbing选项下添加实验性cy.route2()命令。 |